EXHIBIT 99.2
Published on September 2, 2025
Exhibit 99.2

A Late - stage Rare Disease Company Treating Hyperinsulinism Corporate Presentation NASDAQ: RZLT

Forward Looking Statements | 2 This presentation, like many written and oral communications presented by Rezolute and our authorized officers, may contain certain forward - looking statements regarding our prospective performance and strategies within the meaning of Section 27 A of the Securities Act and Section 21 E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 , as amended . We intend such forward - looking statements to be covered by the safe harbor provisions for forward - looking statements contained in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and are including this statement for purposes of said safe harbor provisions . Forward - looking statements, which are based on certain assumptions and describe future plans, strategies, and expectations of Rezolute, are generally identified by use of words such as "anticipate," "believe," "estimate," "expect," "intend," "plan," "project," "prove," "potential," "seek," "strive," "try," or future or conditional verbs such as "predict," "could," "may," "likely," "should," "will," "would," or similar expressions . These Forward - Looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements regarding the sunRIZE clinical study, the RIZE study, the complete removal of the partial clinical holds on RZ 358 for the treatment of hypoglycemia, the Investigational New Drug (IND) application for RZ 358 (ersodetug), the ability of RZ 358 to become an effective treatment, the effectiveness or future effectiveness of RZ 358 as a treatment, statements regarding clinical trial timelines for the treatment . Our ability to predict results or the actual effects of our plans or strategies is inherently uncertain . Accordingly, actual results may differ materially from anticipated results . Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward - looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this release . Except as required by applicable law or regulation, Rezolute undertakes no obligation to update these forward - looking statements to reflect events or circumstances that occur after the date on which such statements were made . Important factors that may cause such a difference include any other factors discussed in our filings with the SEC, including the Risk Factors contained in the Rezolute’s Annual Report on Form 10 - K and Quarterly Reports on Form 10 - Q, which are available at the SEC’s website at www . sec . gov . You are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward - looking statements in this release and are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward - looking statements, which are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement . This presentation shall not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy, nor shall there be any sale of these securities in any state or other jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the securities laws of any such state or other jurisdiction .

Seasoned management team with demonstrated success from early development through commercialization Total $1B+ global market opportunity with additional upside with market expansion Compelling real - world evidence of patient benefit under the Company’s Expanded Access Program Two rare disease Phase 3 programs evaluating ersodetug to treat hypoglycemia in congenital HI and tumor HI RZ358 (ersodetug) is an antibody designed to treat hypoglycemia caused by all forms of hyperinsulinism (HI) A Rare Disease Company Treating Hyperinsulinism | 3 $180 million in cash with runway to mid - 2027
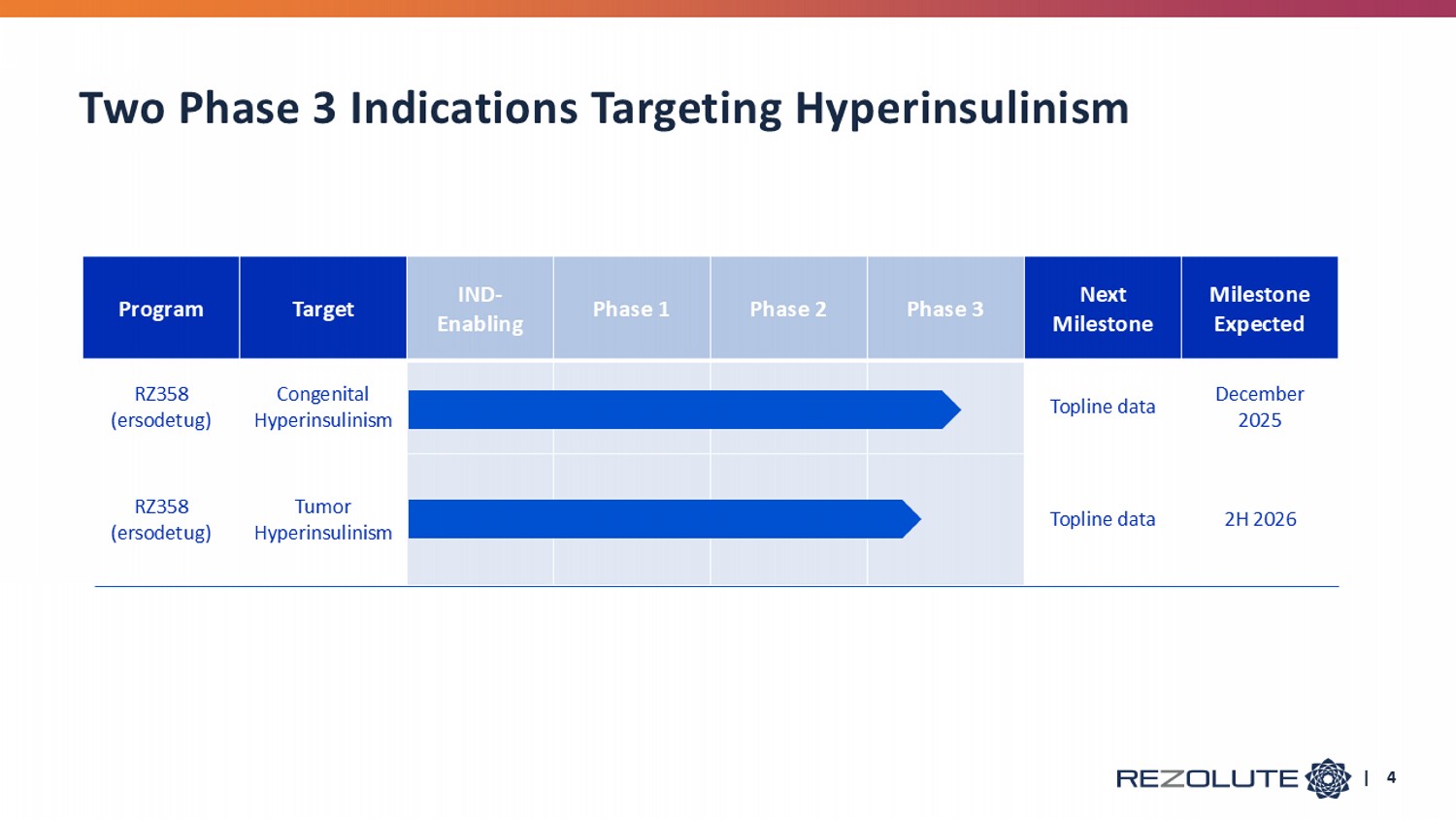
Milestone Expected Next Milestone Phase 3 Phase 2 Phase 1 IND - Enabling Target Program December 2025 Topline data Congenital Hyperinsulinism RZ358 (e rsodetug ) 2H 2026 Topline data Tumor Hyperinsulinism RZ358 (e rsodetug ) Two Phase 3 Indications Targeting Hyperinsulinism | 4

RZ358 Treatment for Hyperinsulinism (HI) E rsodetug
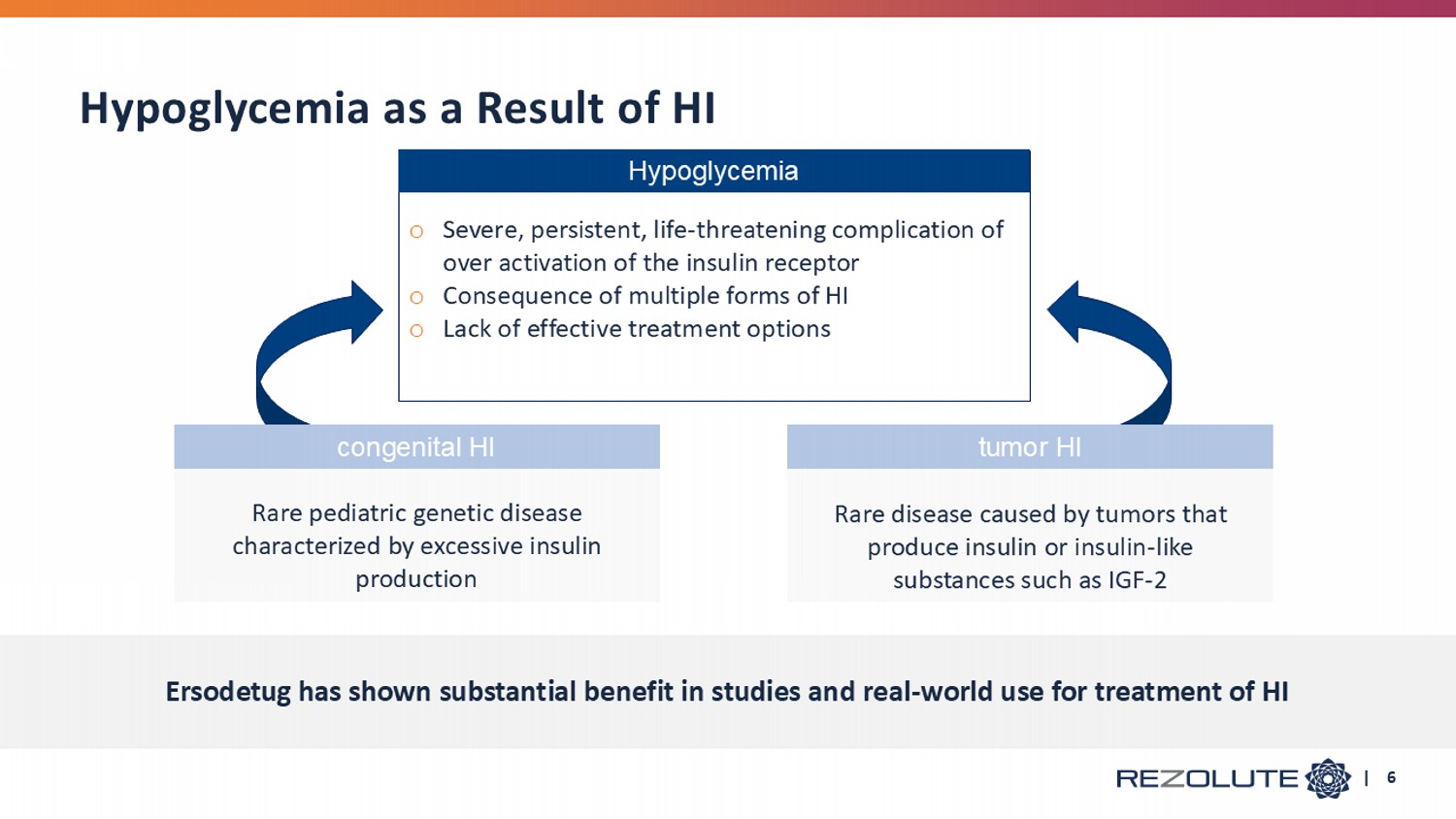
Rare disease caused by tumors that produce insulin or insulin - like substances such as IGF - 2 Rare pediatric genetic disease characterized by excessive insulin production Hypoglycemia as a Result of HI c ongenital HI t umor HI Ersodetug has shown substantial benefit in studies and real - world use for treatment of HI | 6 Hypoglycemia o Severe, persistent, life - threatening complication of over activation of the insulin receptor o Consequence of multiple forms of HI o Lack of effective treatment options
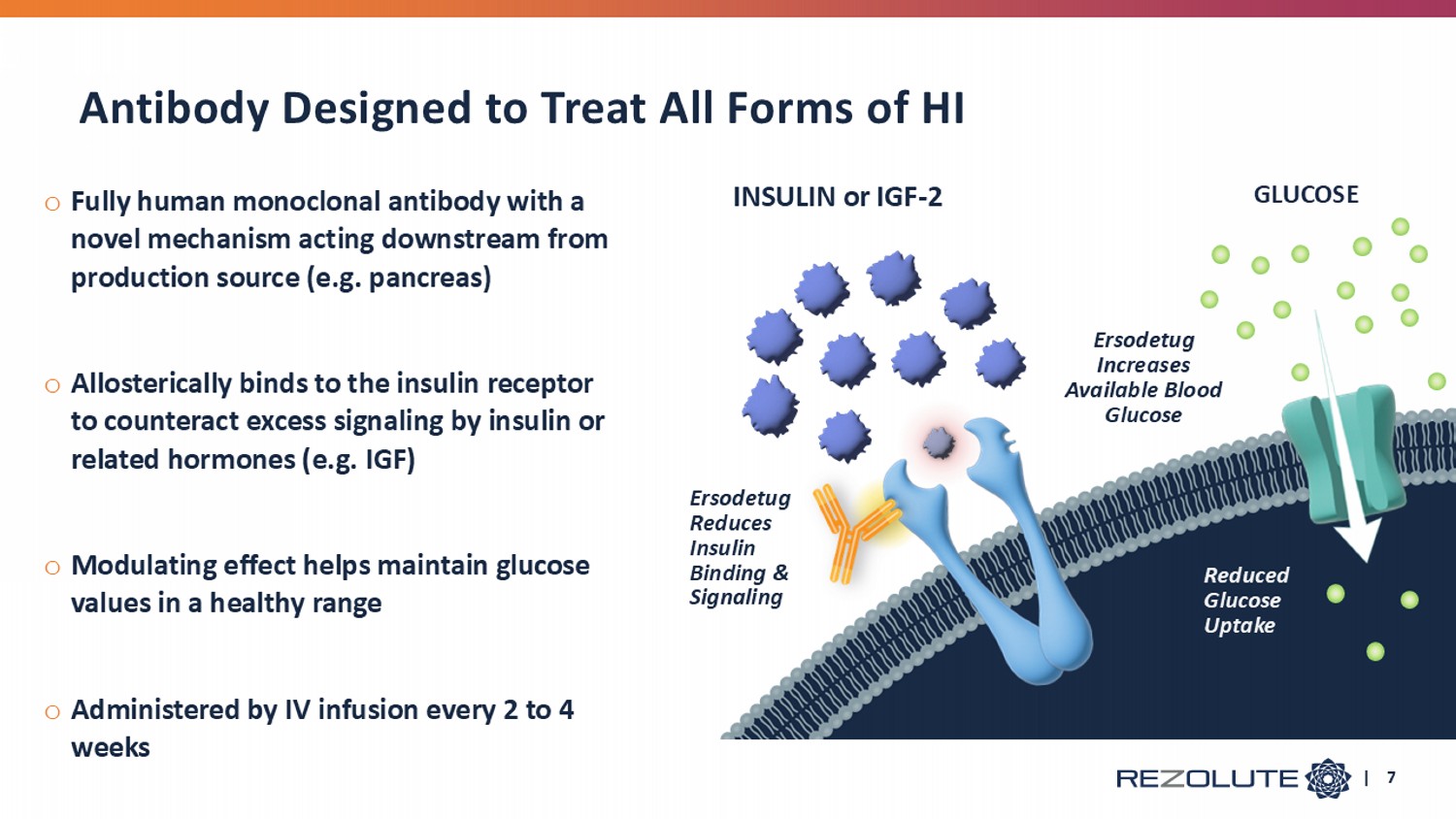
| 7 o Fully human monoclonal antibody with a novel mechanism acting downstream from production source (e.g. pancreas) o Allosterically binds to the insulin receptor to counteract excess signaling by insulin or related hormones (e.g. IGF) o Modulating effect helps maintain glucose values in a healthy range o Administered by IV infusion every 2 to 4 weeks INSULIN or IGF - 2 GLUCOSE Ersodetug Reduces Insulin Binding & Signaling Ersodetug Increases Available Blood Glucose Reduced Glucose Uptake Antibody Designed to Treat All Forms of HI

Congenital HI Congenital HI
o 1 in 28,000 live births in the US 1 , translating to approximately 130 new patients per year o Often presents within first month of life o Most common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infants and children o Requires constant monitoring as serious hypoglycemic lows are often missed o Risk of coma, death, and other serious complications o 50% of children have neurological deficiencies caused by hypoglycemic lows o No therapy has been developed and approved for chronic treatment 2 Disease Background | 9 Source: 1) The birth prevalence of congenital hyperinsulinism: a narrative review of the epidemiology of a rare disease: https://www.rezolutebio.com/wp - content/uploads/2024/06/The - birth - prevalence - of - congenital - hyperinsulinism_a - narrative - review - of - the - epidemiology - of - a - rare - disease.pdf . 2) Based on the RIZE clinical trial outcomes and the evidence of benefit in this serious condition with substantial unmet m edi cal need, ersodetug was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a priority medicines (PRIME) desig nat ion by the European Medicines Agency (EMA), an Innovation Passport designation by the U.K. Innovative Licensing and Access Pathway (ILAP) Steering Group, and Orphan Drug Designation in the US and EU for the trea tme nt of hypoglycemia due to congenital HI.
o Diazoxide (DZ) is first line treatment and the only approved medication for hypoglycemia caused by HI • 60% of patients do not respond to DZ • May experience frequent and serious adverse reactions including volume overload, heart failure, and pulmonary hypertension • Patients report 1 intolerable side effects including increased body hair (92%), loss of appetite (43%), swelling (27%), facial changes (27%), and gastrointestinal upset (26%) o Other available treatment options are suboptimal • Glucagon tends to be temporizing and short - term • Somatostatin analogs have marginal efficacy and potentially serious pediatric side effects • Pancreatectomy is an invasive option in DZ non - responsive patients, but frequently requires adjuvant medications until insulin - dependent diabetes eventually ensues • Intensive feeding regimens (e.g. tube feeding) often underlie all of these approaches • Each of these therapies can contribute to a cycle of poor appetite and feeding aversions Inadequate Standard of Care Source: 1) HI Global Registry 2024 Annual Report: 223patients surveyed, 183 have taken DZ. | 10
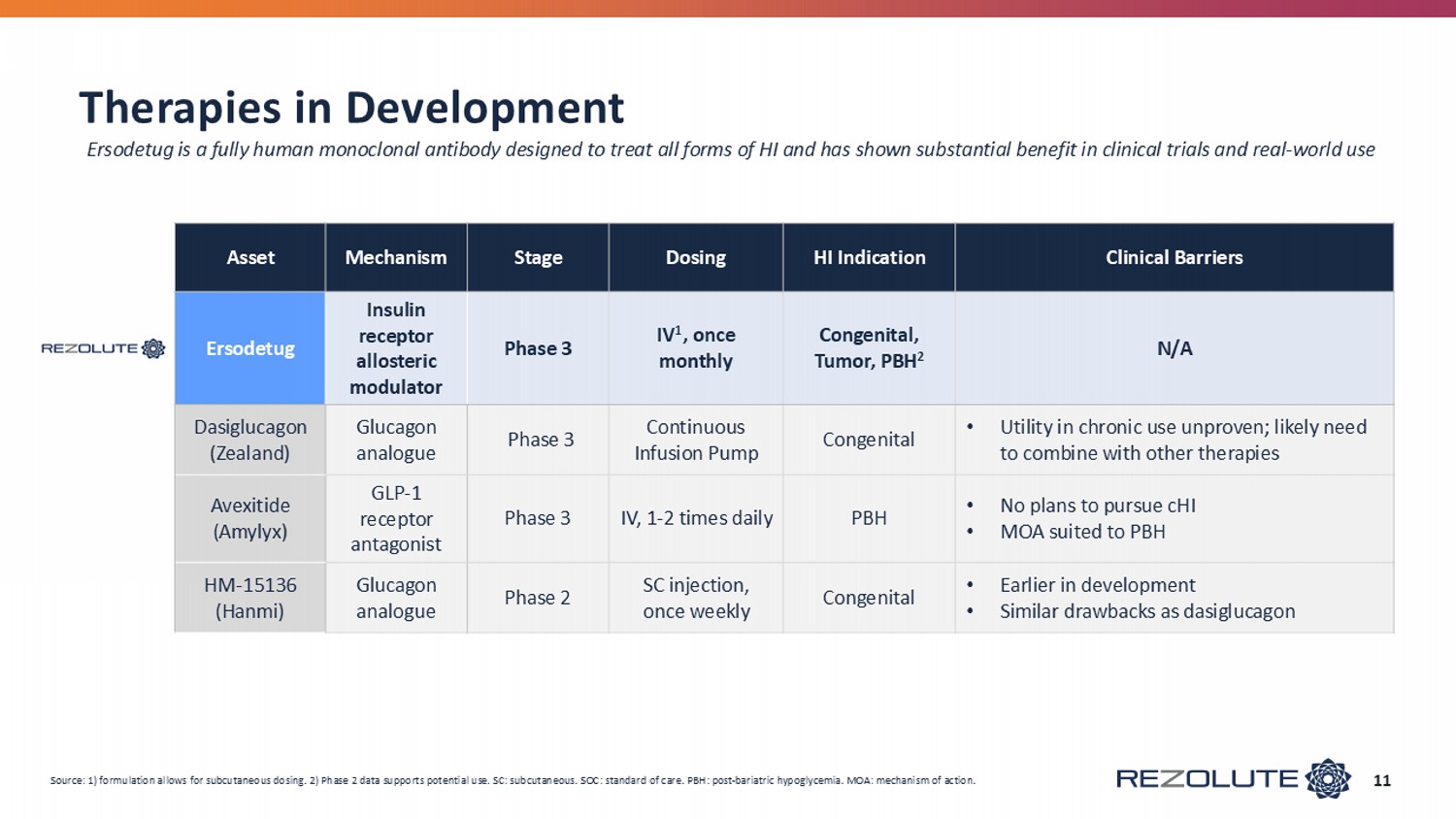
Therapies in Development 11 Clinical Barriers HI Indication Dosing Stage Mechanism Asset N/A Congenital, Tumor, PBH 2 IV 1 , once monthly Phase 3 Insulin receptor allosteric modulator Ersodetug • Utility in chronic use unproven; likely need to combine with other therapies Congenital Continuous Infusion Pump Phase 3 Glucagon analogue Dasiglucagon (Zealand) • No plans to pursue cHI • MOA suited to PBH PBH IV, 1 - 2 times daily Phase 3 GLP - 1 receptor antagonist Avexitide ( Amylyx ) • Earlier in development • Similar drawbacks as dasiglucagon Congenital SC injection, once weekly Phase 2 Glucagon analogue HM - 15136 (Hanmi) Source: 1) formulation allows for subcutaneous dosing. 2) Phase 2 data supports potential use. SC: subcutaneous. SOC: standar d o f care. PBH: post - bariatric hypoglycemia. MOA: mechanism of action. Ersodetug is a fully human monoclonal antibody designed to treat all forms of HI and has shown substantial benefit in clinical trials a nd real - world use

o Global, multi - center, double - blind, randomized, controlled, safety and efficacy registrational study o Patient population (n=56) • Ages 3 months + who do not have adequate glycemic control with standard of care medical management o Primary endpoint: change in average hypoglycemia events per week • Secondary endpoints include change in average daily percent time in hypoglycemia, change in severe hypoglycemia events and time, time in a target glucose range, and symptomatic hypoglycemia events o Pivotal treatment arms • ~48 participants ages 1 year and above randomized in double blind, placebo - controlled fashion • Three bi - weekly loading doses, then 4 monthly doses over a total 6 - month treatment period • 5 mg/kg (+ SOC) (n = 16) • 10 mg/kg (+ SOC) (n = 16) • Placebo (SOC only) (n = 16) • Open label treatment arm: ~8 participants ages 3 months to 1 year • Eligible participants may continue in a long - term extension study following pivotal treatment o Topline results expected December 2025 | 12 Phase 3: The sunRIZE Study SOC: standard of care.
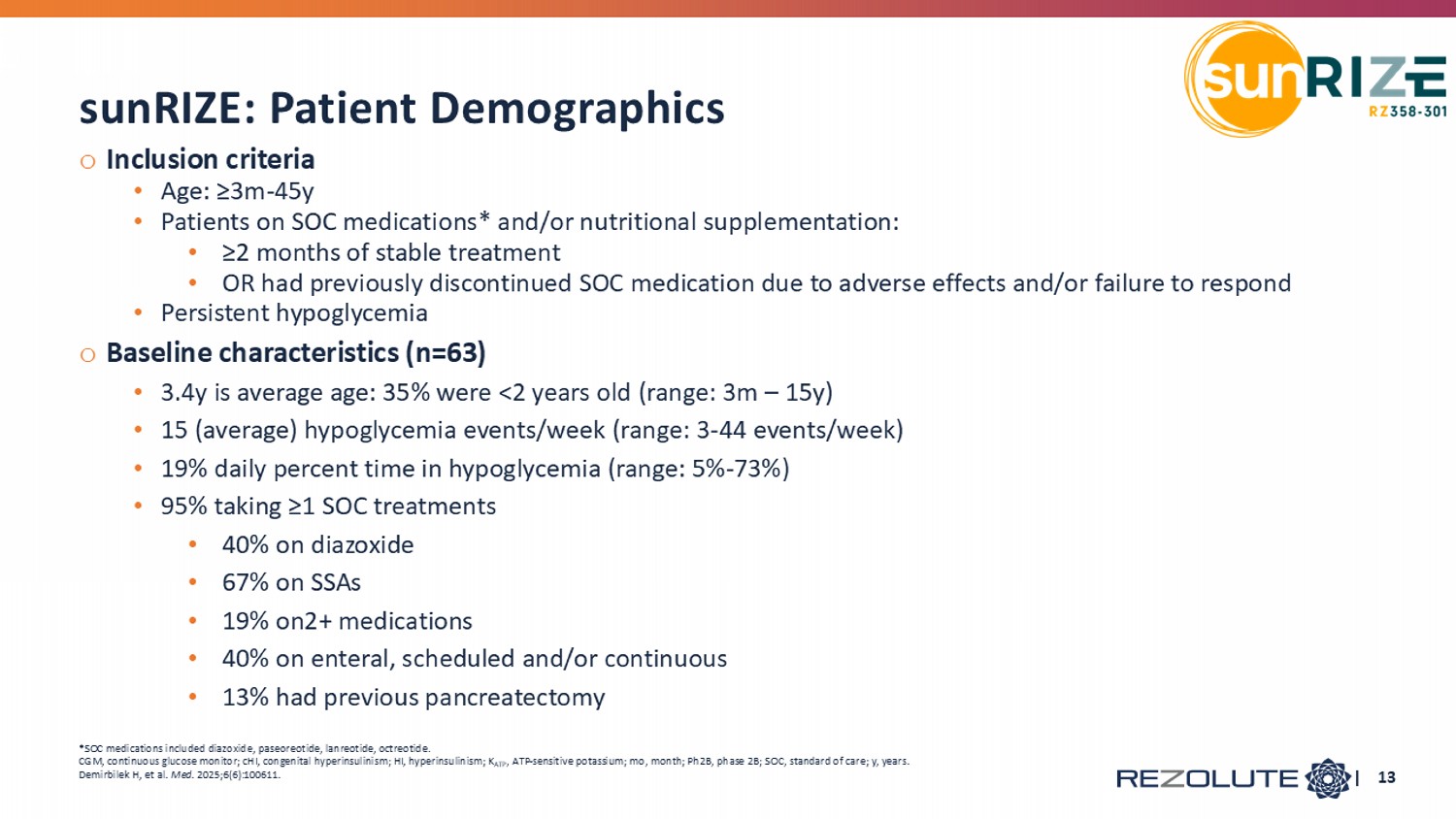
o Inclusion criteria • Age: ≥3m - 45y • Patients on SOC medications* and/or nutritional supplementation: • ≥2 months of stable treatment • OR had previously discontinued SOC medication due to adverse effects and/or failure to respond • Persistent hypoglycemia o Baseline characteristics (n=63) • 3.4y is average age: 35% were <2 years old (range: 3m – 15y) • 15 (average) hypoglycemia events/week (range: 3 - 44 events/week) • 19% daily percent time in hypoglycemia (range: 5% - 73%) • 95% taking ≥1 SOC treatments • 40% on diazoxide • 67% on SSAs • 19% on2+ medications • 40% on enteral, scheduled and/or continuous • 13% had previous pancreatectomy sunRIZE: Patient Demographics *SOC medications included diazoxide, paseoreotide , lanreotide , octreotide. CGM, continuous glucose monitor; cHI, congenital hyperinsulinism; HI, hyperinsulinism; K ATP , ATP - sensitive potassium; mo , month; Ph2B, phase 2B; SOC, standard of care; y, years. Demirbilek H, et al. Med . 2025;6(6):100611. | 13

o 23 participants • Average age ~6.5 ( 16 participants were between 2 - 6 years of age) • Diverse group across gender and genetics o ~20 % average daily time in hypoglycemia and 13 hypoglycemia events per week at baseline • Participants were on standard of care o Predictable and dose - dependent pharmacokinetics o Generally safe and well - tolerated • No adverse drug reactions • No study terminations • No clinically - significant hyperglycemia or hyperglycemia AEs o Study exceeded expectations for glucose correction: • Improvement in hypoglycemia time and events of up to ~ 90 % at top doses • Nearly universal response rate at the top dose | 14 SOC: standard of care. AEs: adverse events. Phase 2b RIZE Study Results
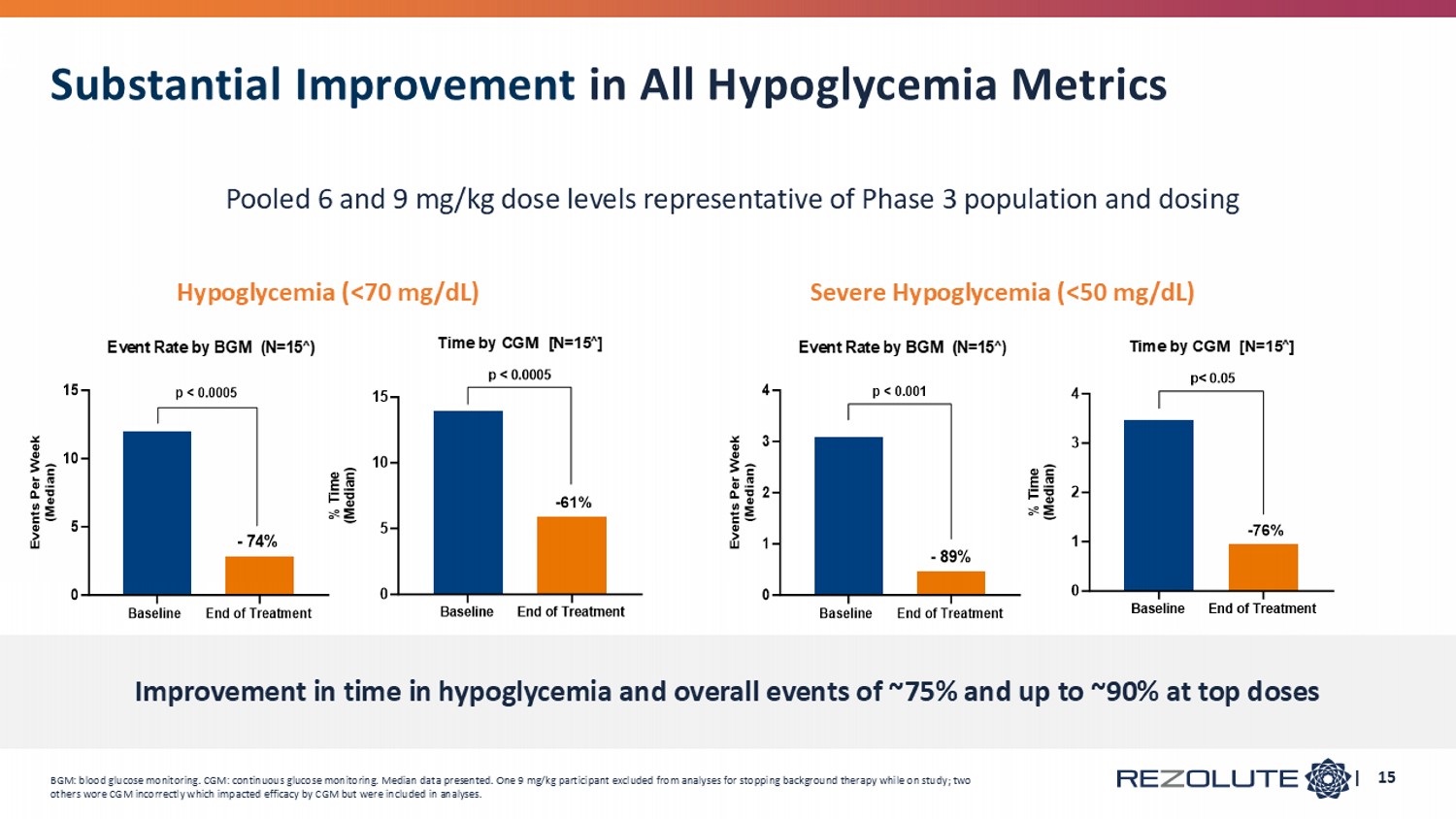
Baseline End of Treatment 0 5 10 15 Time by CGM [N=15 ∧ ] % T i m e ( M e d i a n ) -61% p < 0.0005 Baseline End of Treatment 0 5 10 15 Event Rate by BGM (N=15 ∧ ) E v e n t s P e r W e e k ( M e d i a n ) p < 0.0005 - 74% Hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL) Severe Hypoglycemia (<50 mg/dL) Baseline End of Treatment 0 1 2 3 4 Event Rate by BGM (N=15 ∧ ) E v e n t s P e r W e e k ( M e d i a n ) p < 0.001 - 89% BGM: blood glucose monitoring. CGM: continuous glucose monitoring. Median data presented. One 9 mg/kg participant excluded from analyses for stopping background therapy while on study; two others wore CGM incorrectly which impacted efficacy by CGM but were included in analyses. | 15 Substantial Improvement in All Hypoglycemia Metrics Pooled 6 and 9 mg/kg dose levels representative of Phase 3 population and dosing Improvement in time in hypoglycemia and overall events of ~75% and up to ~90% at top doses
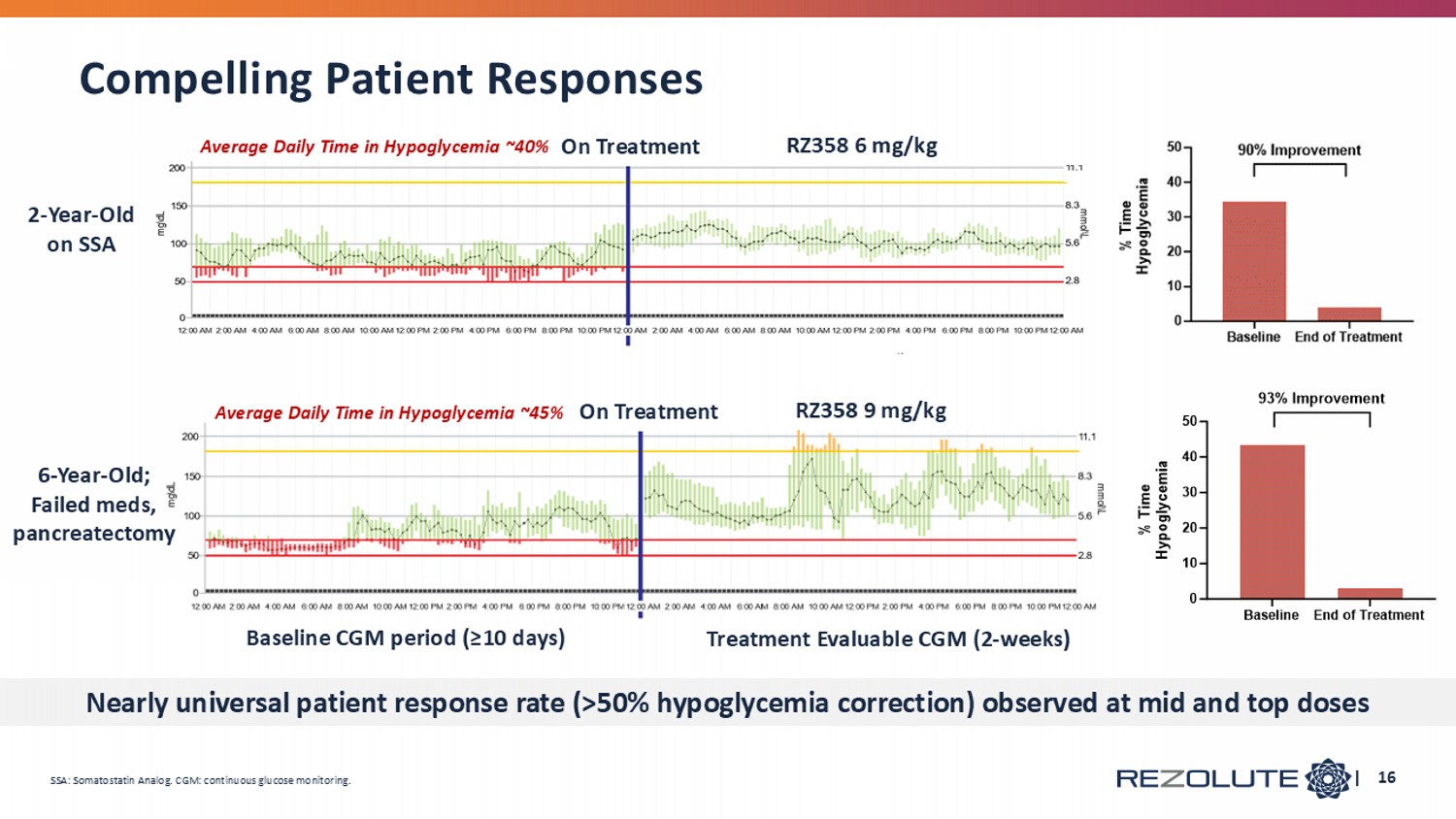
| 16 2 - Year - Old on SSA 6 - Year - Old; Failed meds, pancreatectomy Average Daily Time in Hypoglycemia ~40% Average Daily Time in Hypoglycemia ~45% Baseline CGM period (≥10 days) Treatment Evaluable CGM (2 - weeks) RZ358 9 mg/kg RZ358 6 mg/kg On Treatment On Treatment SSA: Somatostatin Analog. CGM: continuous glucose monitoring. Compelling Patient Responses Nearly universal patient response rate (>50% hypoglycemia correction) observed at mid and top doses
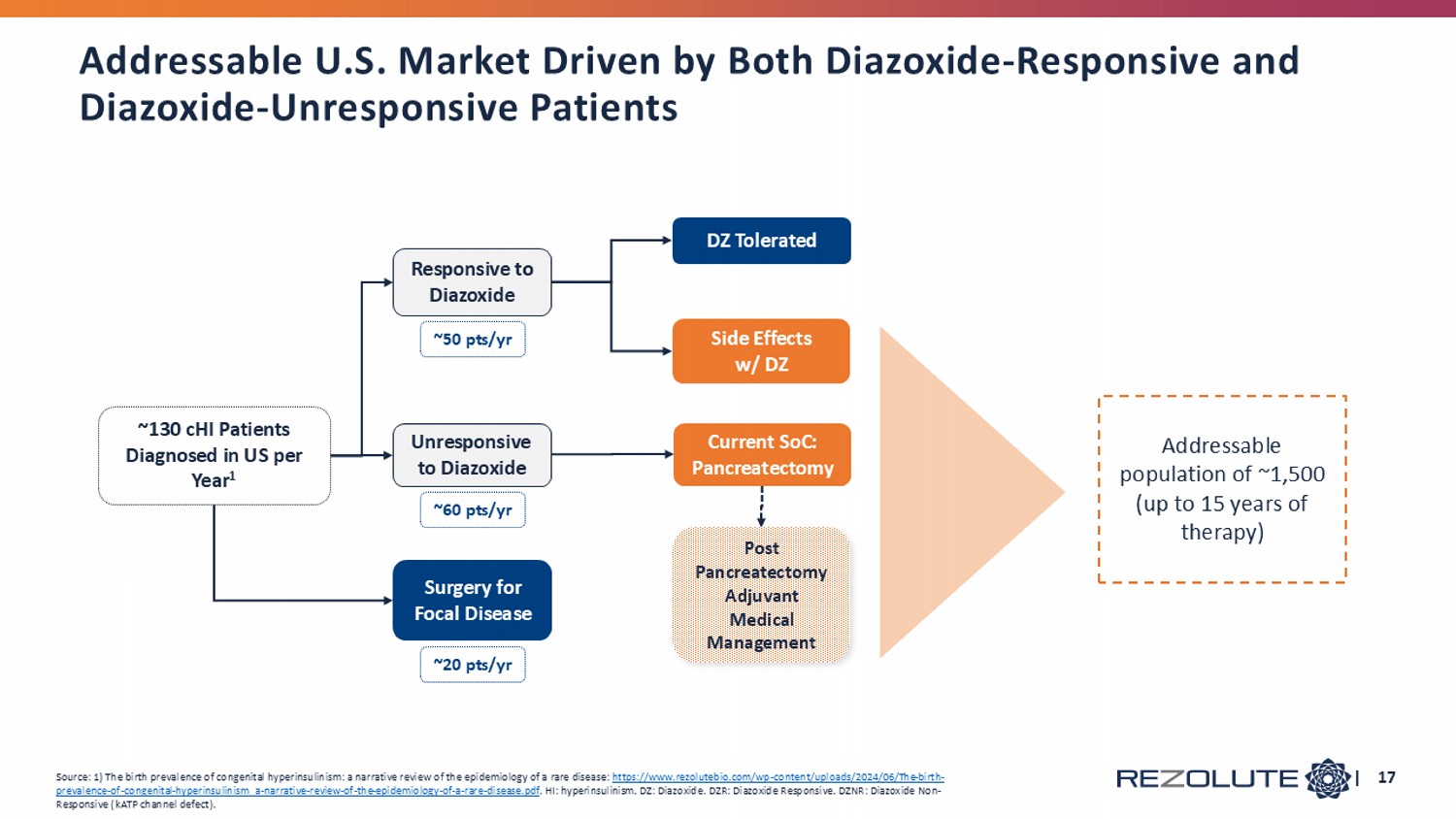
| 17 Side Effects w/ DZ DZ Tolerated Surgery for Focal Disease Current SoC: Pancreatectomy Responsive to Diazoxide Unresponsive to Diazoxide ~130 cHI Patients Diagnosed in US per Year 1 ~20 pts/yr Addressable population of ~1,500 (up to 15 years of therapy) Source: 1) The birth prevalence of congenital hyperinsulinism: a narrative review of the epidemiology of a rare disease: https://www.rezolutebio.com/wp - content/uploads/2024/06/The - birth - prevalence - of - congenital - hyperinsulinism_a - narrative - review - of - the - epidemiology - of - a - rare - disease.pdf . HI: hyperinsulinism. DZ: D iazoxide . DZR : Diazoxide Responsive. DZNR: Diazoxide Non - Responsive ( kATP channel defect). ~50 pts/yr ~60 pts/yr Post Pancreatectomy Adjuvant Medical Management Addressable U.S. Market Driven by Both Diazoxide - Responsive and Diazoxide - Unresponsive Patients

Tumor HI
o Hypoglycemia caused by two distinct tumor types: • Islet Cell Tumors (ICT) • Excessive secretion of insulin • Malignant insulinomas are the most common ICTs that cause hypoglycemia • Non - Islet Cell Tumors (NICT) • Produce and secrete insulin - like substances such as IGF - 2 that over - activate the insulin receptor • Hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) are the most common NICTs that cause hypoglycemia in addition to several other tumor types including fibrosarcomas and mesotheliomas o Significant unmet need across both tumor types • Resulting hypoglycemia is often severe and may have serious adverse outcomes • Limited treatment options with poor efficacy and safety profiles • High morbidity and mortality rates • Can require hospitalization (often prolonged and in ICU) and interferes with patient quality of life • May prevent adjuvant tumor treatment Disease Background | 19
o Tumor - directed therapies do not directly treat hypoglycemia • Adequate hypoglycemia management is required prior to initiation of tumor - targeted therapies o Therapies to treat malignant insulinoma are often ineffective or poorly tolerated • Diazoxide (DZ) is the only approved treatment • Suboptimal response rates and serious side effects • Somatostatin analogs (SSAs) • Used off - label with limited success • May worsen hypoglycemia in tumor HI setting • mTOR - inhibitors • Used off - label and have p otentially severe side effects o Limited and often ineffective treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) • Medical therapies directed at suppressing insulin secretion such as DZ and SSAs do not work in non - islet cell tumors (NICTs) where HI is caused by non - insulin substances such as IGF - 2 Treatment Options and Unmet Need | 20 ICT: islet - cell tumor. NICT: non - islet cell tumor. SOC: standard of care.
o Multiple ICT patients with severe refractory hypoglycemia • H ospitalized and in life - threatening or hospice - bound condition • Required continuous high volume/concentration intravenous dextrose or nutritional infusion • T umor - directed therapies (e.g., embolization, radiotherapy, chemotherapy) deferred because of hypoglycemia • Physician - requested use of ersodetug o Administration of ersodetug resulted in: • Substantial hypoglycemia improvement with no significant side effects 1 • Discontinuation of intravenous dextrose • Discharge from in - patient to out - patient care • R esumption of tumor - directed therapies Real - world Patient Benefit in Expanded Access Program of Ersodetug | 21 1) Based on real - world patient benefit demonstrated in Expanded Access Program the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Orphan Drug Designation to ersodetug for the treatment of hypoglycemia due to tumor HI. Sources: n engl j med 389;8 Aug24,2023 - https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2307576?query=TOC&cid=NEJM+eToc%2C+August+24%2C+2023+DM2279684_NEJM_Non_Subscriber &bi d=1754093795

o Global, multi - center, single - arm, open - label registrational study o Patient population (n=~16) • Adult ICT and NICT patients with HI who have not achieved adequate hypoglycemia control with SOC therapies o Primary endpoint: number of participants achieving ≥50% reduction from baseline IV glucose requirements (glucose infusion rate; GIR) • Additional endpoints include number of participants and time to discontinuation of GIR, time to discharge from the hospital, extent of hypoglycemia events and hypoglycemia time in the outpatient setting by self - monitored blood glucose and continuous glucose monitor, respectively, and patient reported quality of life. o Treatment arms and dosing regimen • Treatment arms and dosing regimen • Once weekly administration over 8 - week pivotal treatment period • 9 mg/kg per week as add - on to SOC • All participants may receive ersodetug in long - term extension o Topline results expected second half of 2026 | 22 Phase 3: The upLIFT Study ICT: islet - cell tumor. NICT: non - islet cell tumor. SOC: standard of care.

Phase 3 Study Overview o Multi - center, double - blind, randomized, controlled, safety and efficacy registrational study o Patient population (n= up to 48) • Adult ICT and NICT patients with HI who have not achieved adequate hypoglycemia control with SOC therapies • 24 participants in double - blind, placebo - controlled arm (to evaluate primary endpoint/hypoglycemia events) • Up to 24 participants in open label arm: initial 6 NICT patients and any hospitalized participants on IV glucose o Primary endpoint: change in average hypoglycemia events per week by self - monitored blood glucose • Secondary/additional endpoints: change in average daily percent time in hypoglycemia, change in Level 1 hypoglycemia events and time, hospitalization, patient reported quality of life • Open - label arm to evaluate change in IV glucose requirements in hospitalized participants o Treatment arms and dosing regimen • Once weekly administration over 8 - week pivotal treatment period • 9 mg/kg RZ358 (+ SOC) (n = 12) • Matched placebo (SOC only) (n = 12) • 9 mg/kg RZ358 Open Label Arm (n ≤ 24) • Eligible participants may continue in a long - term extension study following pivotal treatment o IND filed and cleared: start - up activities in progress to enable patient enrollment in 1H 2025 ICT: islet - cell tumor. NICT: non - islet cell tumor. SOC: standard of care. | 23
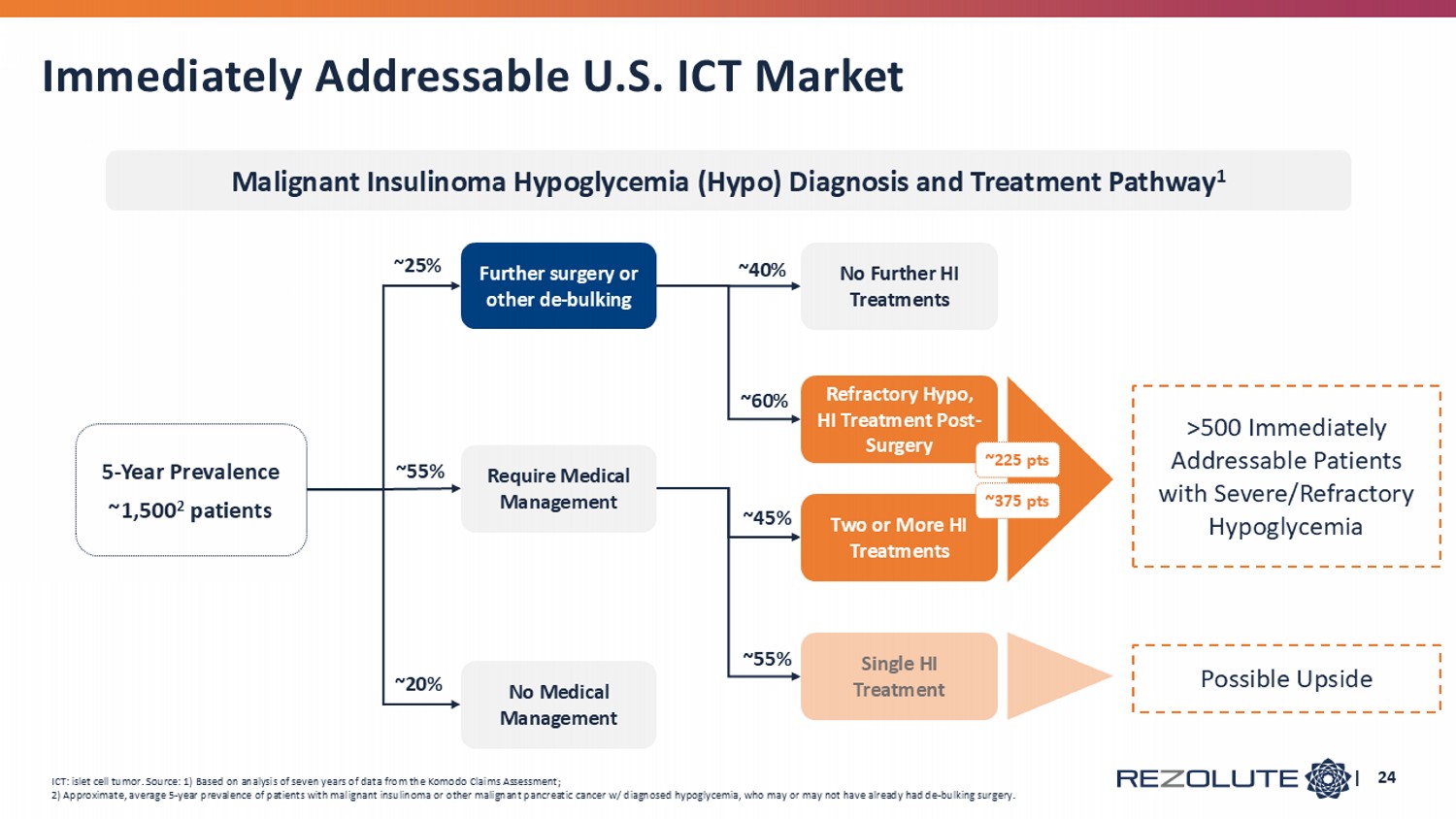
Immediately Addressable U.S. ICT Market | 24 ~25 % 5 - Year Prevalence ~1,500 2 patients >500 Immediately Addressable Patients with Severe/Refractory Hypoglycemia Malignant Insulinoma Hypoglycemia (Hypo) Diagnosis and Treatment Pathway 1 ICT: islet cell tumor. Source: 1) Based on analysis of seven years of data from the Komodo Claims Assessment; 2) Approximate, average 5 - year prevalence of patients with malignant insulinoma or other malignant pancreatic cancer w/ diagnose d hypoglycemia, who may or may not have already had de - bulking surgery. No Medical Management ~2 0% Further surgery or other de - bulking Two or More HI Treatments Require Medical Management ~55 % Refractory Hypo, HI Treatment Post - Surgery No Further HI Treatments ~40% ~60 % ~225 pts ~375 pts Single HI Treatment Possible Upside ~45 % ~55 %
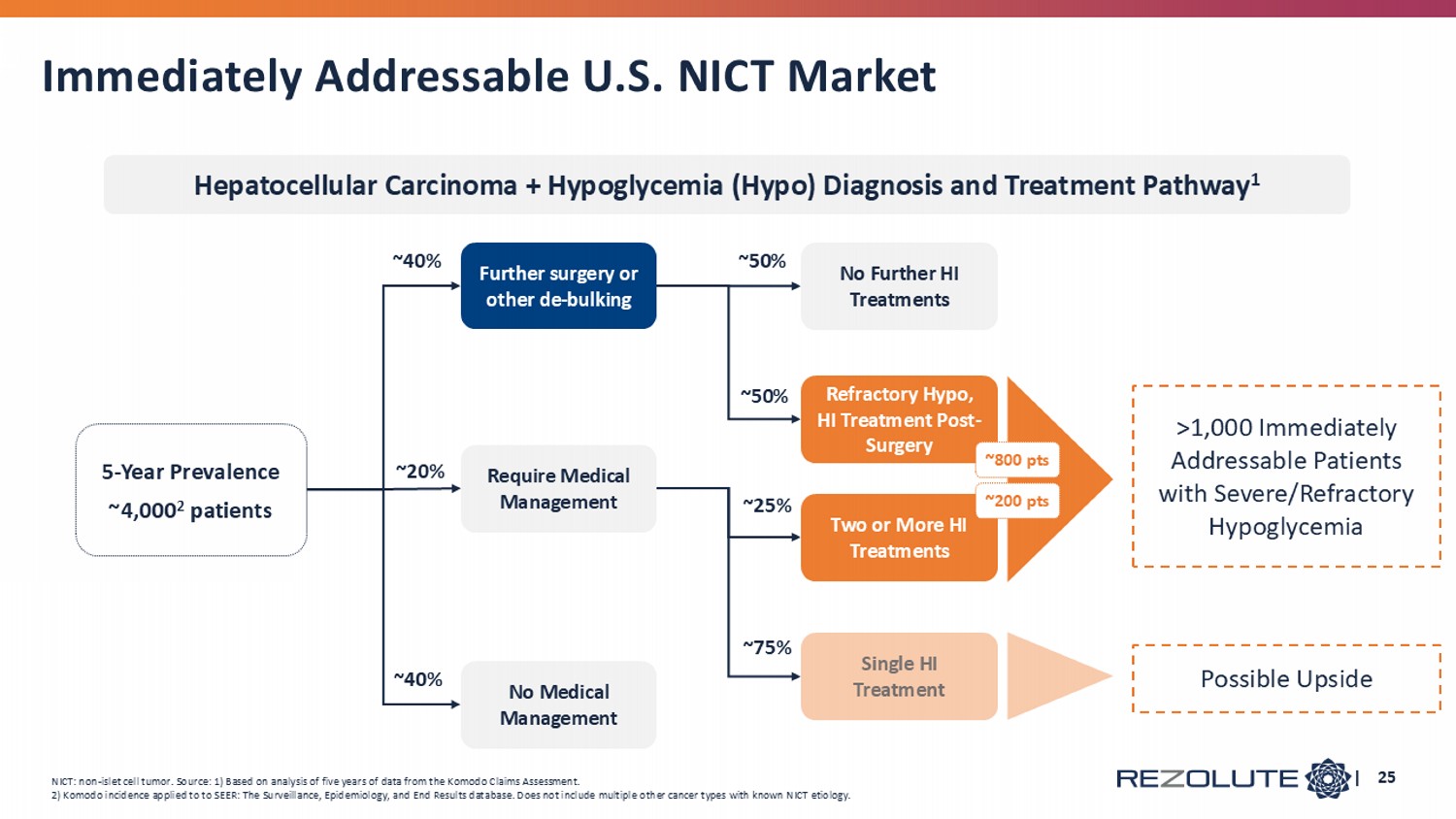
Immediately Addressable U.S. NICT Market | 25 ~40 % 5 - Year Prevalence ~4,000 2 patients >1,000 Immediately Addressable Patients with Severe/Refractory Hypoglycemia No Medical Management ~4 0% Further surgery or other de - bulking Two or More HI Treatments Require Medical Management ~20 % Refractory Hypo, HI Treatment Post - Surgery No Further HI Treatments ~50% ~50 % ~800 pts ~200 pts Single HI Treatment Possible Upside ~25 % ~75 % NICT: non - islet cell tumor. Source: 1) Based on analysis of five years of data from the Komodo Claims Assessment. 2) Komodo incidence applied to to SEER: The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Does not include multiple o the r cancer types with known NICT etiology. Hepatocellular Carcinoma + Hypoglycemia (Hypo) Diagnosis and Treatment Pathway 1

o Potential to Address Two Rare Disease Markets • ~1,500 addressable cHI patients in US; equivalent patient population in Europe • >500 islet cell tumor patients and >1,000 n on - islet c ell tumor patients addressable in the US o Highly Concentrated Physician Base for cHI • 60% of patients are diagnosed within 1 month of presentation • 80% of addressable patients are seen by centers of excellence (many participating in sunRIZE study) o Tumor HI Patients Identified and treated by both Endocrinologists and Oncologists o Regulatory Designations: Breakthrough Therapy (FDA), Orphan, Pediatric Rare Disease (FDA), PRIME (EMA), ILAP (UK) | 26 HI: hyperinsulinism. Commercial Opportunity $1B+ global market opportunity across two indications with rare disease drug pricing
Total $1B+ global market opportunity with additional upside with market expansion Compelling real - world evidence of patient benefit under the Company’s Expanded Access Program RZ358 ( ersodetug ) is an antibody designed to treat hypoglycemia caused by all forms of HI Mission - driven to improve outcomes for individuals with severe hypoglycemia caused by hyperinsulinism (HI) A Rare Disease Company Treating Hyperinsulinism | 27 $180 million in cash with runway to mid - 2027
